

Please be sure that the supposed source of the copyright violation is not itself a Wikipedia mirror.
#MD SIMULATION FDTD FREE#
Please review the source and remedy this by editing this article to remove any non-free copyrighted content and attributing free content correctly, or flagging the content for deletion. This section may have been copied and pasted from another location, possibly in violation of Wikipedia's copyright policy.
#MD SIMULATION FDTD SOFTWARE#
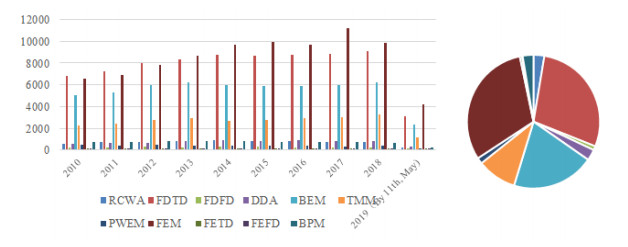
As of 2013, there are at least 25 commercial/proprietary FDTD software vendors 13 free-software/ open-source-software FDTD projects and 2 freeware/closed-source FDTD projects, some not for commercial use (see External links).ĭevelopment of FDTD and Maxwell's equations In 2006, an estimated 2,000 FDTD-related publications appeared in the science and engineering literature (see Popularity). Current FDTD modeling applications range from near- DC (ultralow-frequency geophysics involving the entire Earth- ionosphere waveguide) through microwaves (radar signature technology, antennas, wireless communications devices, digital interconnects, biomedical imaging/treatment) to visible light ( photonic crystals, nano plasmonics, solitons, and biophotonics). Since about 1990, FDTD techniques have emerged as primary means to computationally model many scientific and engineering problems dealing with electromagnetic wave interactions with material structures. The descriptor "Finite-difference time-domain" and its corresponding "FDTD" acronym were originated by Allen Taflove in 1980. The novelty of Kane Yee's FDTD scheme, presented in his seminal 1966 paper, was to apply centered finite difference operators on staggered grids in space and time for each electric and magnetic vector field component in Maxwell's curl equations.
In finite-difference time-domain method, "Yee lattice" is used to discretize Maxwell's equations in space.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
